INCITE TECHNOLOGY
TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW
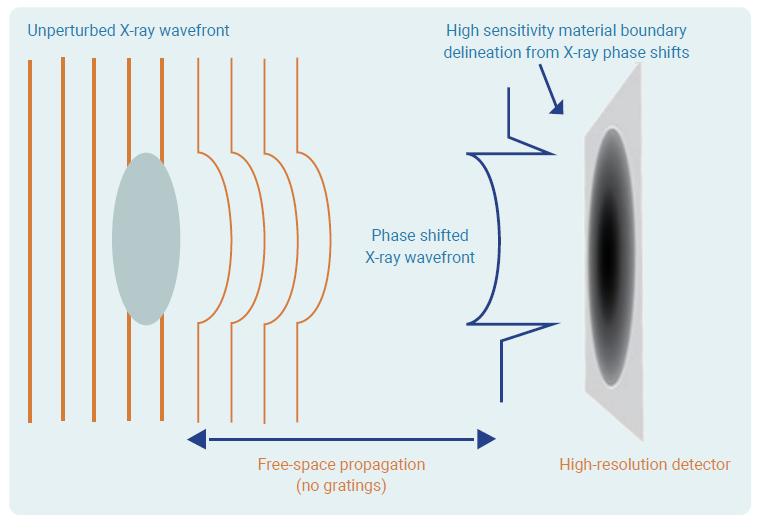
What is phase contrast technology?
Materials with poor X-ray absorption can be challenging for conventional X-ray imaging devices. However, objects visualized by propagation-based X-ray imaging will exhibit absorption contrast as well as phase contrast information. The phase contrast is a direct result of free-space propagation of the X-ray beam, transforming X-ray phase changes at the object plane into X-ray intensity variations in the image plane. Propagation-based phase contrast X-ray imaging can result in increased contrast at object boundaries for better detectability of materials with poor X-ray absorption.
BRILLIANSE™: NOVEL DETECTION TECHNOLOGY
The hybrid a-Se/CMOS detector uses an a-Se photoconductor with high intrinsic spatial resolution for direct conversion of X-ray photons to electric charge. The electronic signal is then read out by a low noise CMOS active pixel sensor (APS). Without the need to first convert X-ray photons to visible light, as in indirect scintillator-based approaches, thinning of the conversion layer to minimize optical scatter is not necessary.
The direct conversion approach allows a thick conversion layer and operation at 100% fill factor for high DQE. At 35 keV, BrillianSe™ has a market leading combination of high DQE (40% at 10 cycles/mm) and a small point-spread function (PSF) (1.1 pixel). This facilitates imaging for low flux applications such as X-ray diffraction, dose sensitive protein crystallography or throughput-limited imaging of materials with and without phase-contrast.
Learn more: inCiTe Technical Note
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Abbaszadeh, CC Scott, OBubon, A Reznik, KS Karim, “Enhanced detection efficiency of direct conversion X-ray detector using polyimide as hole-blocking layer,” Scientific Reports, December 2013
G.P. Lindberg, T. O’Loughlin, N. Gross, A. Mishchenko, A. Reznik, S. Abbaszadeh, K.S. Karim, G. Belev, B. Weinstein, “Photo-crystallization in a-Se layer structures: effects of film-substrate interface-rigidity,” Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 116, November 2014.
Parsafar, C. Scott, A. El-Falou, P. Levine, K.S. Karim, “Direct-Conversion CMOS X-Ray Imager with 5.6μm × 6.25 μm Pixels,” IEEE Electron Device Letters, 36(5), pp. 481-3, May 2015.
C.C. Scott, A. Parsafar, A. El-Falou, P. M. Levine, K.S. Karim, “High Dose Efficiency, Ultra-high Resolution Amorphous Selenium/CMOS Hybrid Digital X-ray Imager,” IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) Technical Digest, December 2015.
Pil-Ali, A., Adnani, S. & Karim, K.S. Self-aligned multi-layer X-ray absorption grating using large-area fabrication methods for X-ray phase-contrast imaging. Sci Rep 13, 2508 (2023)
RELATED RESEARCH
Comparing conventional and phase contrast imaging
Gureyev, Timur Eugenievich, Sheridan C. Mayo, Damian E. Myers, Ya Nesterets, D. M. Paganin, A. Pogany, Andrew W. Stevenson, and S. W. Wilkins. “Refracting Röntgen’s rays: propagation-based x-ray phase contrast for biomedical imaging.” Journal of Applied Physics 105, no. 10 (2009): 102005.
Krenkel, Martin, Mareike Töpperwien, Christian Dullin, Frauke Alves, and Tim Salditt. “Propagation-based phase-contrast tomography for high-resolution lung imaging with laboratory sources.” AIP Advances 6, no. 3 (2016): 035007.
Olivo, A., and E. Castelli. “X-ray phase contrast imaging: From synchrotrons to conventional sources.” La Rivista Del Nuovo Cimento 37 (2014): 467-508.
Bravin, Alberto, Paola Coan, and Pekka Suortti. “X-ray phase-contrast imaging: from pre-clinical applications towards clinics.” Physics in Medicine & Biology 58, no. 1 (2012): R1.
Bidola, P., K. Morgan, M. Willner, A. Fehringer, S. Allner, F. Prade, F. Pfeiffer, and K. Achterhold. “Application of sensitive, high‐resolution imaging at a commercial lab‐based X‐ray micro‐CT system using propagation‐based phase retrieval.” Journal of Microscopy 266, no. 2 (2017): 211-220.
Propagation
Wilkins, S. W., T. Ei Gureyev, D. Gao, A. Pogany, and A. W. Stevenson. “Phase-contrast imaging using polychromatic hard X-rays.” Nature 384, no. 6607 (1996): 335-338.
Mayo, Sheridan C., Andrew W. Stevenson, and Stephen W. Wilkins. “In-line phase-contrast X-ray imaging and tomography for materials science.” Materials 5, no. 5 (2012): 937-965.
Gratings
Pfeiffer, Franz, Timm Weitkamp, Oliver Bunk, and Christian David. “Phase retrieval and differential phase-contrast imaging with low-brilliance X-ray sources.” Nature physics 2, no. 4 (2006): 258-261.
Media Inquiries
